Story Highlights
- One in 10 parents say their child has voiced concerns about safety
- Mothers, nonwhite parents most likely to worry about school safety
WASHINGTON, D.C. -- Twenty-nine percent of U.S. parents say they fear for their child's safety at school. This is down from the 33% found immediately after the Sandy Hook school shooting in Newtown, Connecticut, in December 2012, but still above the 25% measured a few months before that incident occurred.
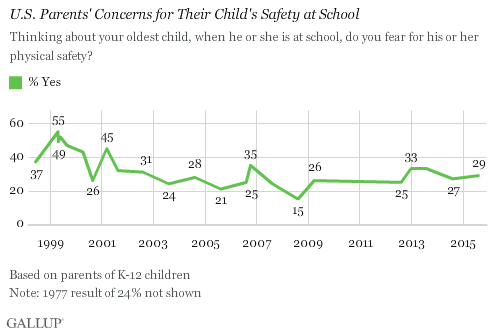
U.S. parents' fears about school safety reached a high of 55% in April 1999 after the Columbine High School massacre in Colorado. Parents' concern typically peaks immediately following high-profile shootings -- as seen in 2001 (45%) after the Santana High School shooting in California, and in 2006 (35%) after a shooting in an Amish schoolhouse in Pennsylvania -- and then fades. The low point in parental concern (15%) came in August 2008.
The latest results come from Gallup's Work and Education poll, conducted Aug. 5-9.
Safety and gun control have been at the forefront of news coverage and legislative debate in recent years, as shootings in and out of schools have rocked communities. The tragedy at Sandy Hook initiated an intense legislative debate on gun control, but less than a year after the incident, .
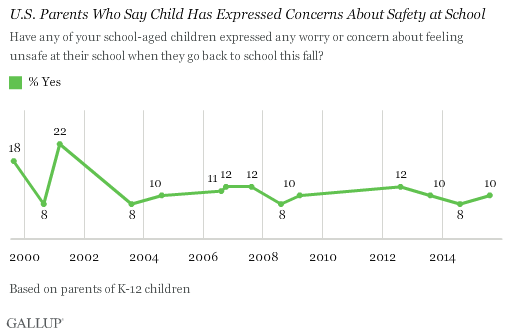
One in 10 Parents Say Child Has Expressed Concerns About Safety at School
Ten percent of U.S. parents of K-12 students say their child has expressed worries about his or her safety at school. This figure has been fairly consistent since 2003, never straying from the 8% to 12% range.
In the early post-Columbine years, parents were more likely to report hearing such concerns, with one in five saying so in 1999 and in 2001.
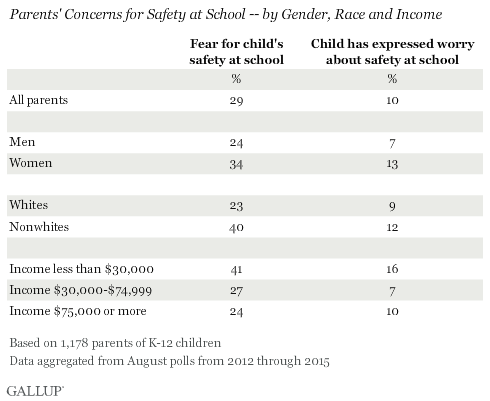
Women, Nonwhites and Lower-Income Parents Most Likely to Worry About Safety
To analyze parents' concerns about school safety by subgroup, 优蜜传媒aggregated data from the last five surveys going back to August 2012, when the percentage fearing for their child's safety averaged 25%.
Mothers of K-12 students (34%) are more likely than fathers (24%) to worry about their child's safety at school. And mothers are about twice as likely as fathers to report that their child has expressed concerns about school safety.
Four in 10 nonwhite parents worry about their child's safety at school, far higher than the 23% of white parents who worry. However, the percentage of white (9%) and nonwhite parents (12%) who say their child has voiced concerns about school safety is similar.
Parents earning less than $30,000 per year in annual household income are more likely than parents who earn more to worry about their child's safety and to say their child has expressed concerns about school safety.
Bottom Line
Three in 10 parents worry about their child's physical safety at school, and they are not without reason. According to a , the number of school killings in the U.S. between 2000 and 2010 was one less than the number in dozens of other countries combined.
The most horrifying acts of violence at U.S. schools can leave temporary impressions on parents' psyches. The early 2000s, which were just as much the post-9/11 years as they were the post-Columbine years, ranked high for parental anxiety about school safety, but by 2005, worries for children's safety at school had hit a new low. And despite the unprecedented shock of Sandy Hook, parents' worries are now similar to their historical averages.
Historical data for this question is available in .
Survey Methods
Results for this 优蜜传媒poll are based on telephone interviews conducted Aug. 5-9, 2015, on the 优蜜传媒U.S. Daily survey, with a random sample of 213 K-12 parents, aged 18 and older, living in all 50 U.S. states and the District of Columbia. For results based on the total sample of parents, the margin of sampling error is ±9 percentage points at the 95% confidence level. All reported margins of sampling error include computed design effects for weighting.
Subgroup analysis represents aggregated data from 2012 to 2015. For results based on the total sample of 645 fathers, the margin of sampling error is ±5 percentage points at the 95% confidence level. For results based on the total sample of 533 mothers, the margin of sampling error is ±5 percentage points at the 95% confidence level. For results based on the total sample of 854 whites, the margin of sampling error is ±4 percentage points at the 95% confidence level. For results based on the total sample of 296 nonwhites, the margin of sampling error is ±7 percentage points at the 95% confidence level. For results based on the total sample of 197 parents whose households earn less than $30,000, the margin of sampling error is ±9 percentage points at the 95% confidence level. For results based on the total sample of 409 parents whose households earn between $30,000 and $74,999, the margin of sampling error is ±6 percentage points at the 95% confidence level. For results based on the total sample of 490 parents whose households earn $75,000 or more, the margin of sampling error is ±5 percentage points at the 95% confidence level.
Each sample of national adults includes a minimum quota of 50% cellphone respondents and 50% landline respondents, with additional minimum quotas by time zone within region. Landline and cellular telephone numbers are selected using random-digit-dial methods.
Learn more about how the works.
