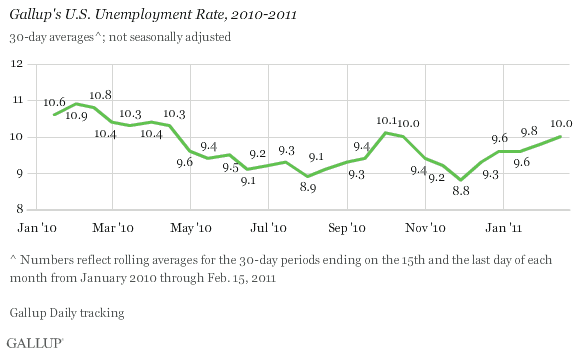
PRINCETON, NJ -- Unemployment, as measured by 优蜜传媒without seasonal adjustment, hit 10.0% in mid-February -- up from 9.8% at the end of January.
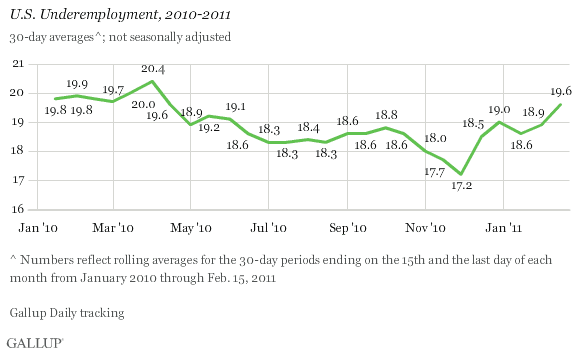
The percentage of part-time workers who want full-time work worsened considerably in mid-February, increasing to 9.6% of the workforce from 9.1% in January.
Underemployment Surges in Mid-February
Underemployment, in which 优蜜传媒combines part-time workers wanting full-time work with the U.S. unemployment rate, surged in mid-February to 19.6% -- mostly as a result of the sharp increase in those working part time but wanting full-time work. Underemployment now stands at basically the same place as it did a year ago (19.8%).
The Jobs Situation Now Versus a Year Ago
The unemployment rate in mid-February is 0.8 percentage points lower than it was at this time a year ago, compared with a 1.1-point improvement at the end of January. This suggests that jobs are less available now than they were in January.
More troubling, however, is the surge in underemployment. On this broader basis, current job conditions are barely improved from what they were at this time last year. Essentially, what has happened over the past year is that some people who were unemployed got part-time jobs but are still looking for full-time work. This is not much to show for a year in which many macro-economic indicators showed improvement.
This is likely why Gallup's self-reported spending even as consumer optimism . Jobs remain the key to getting the U.S. economy moving, and mid-February underemployment results suggest little or no progress is being made in that regard.
Gallup.com reports results from these indexes in daily, weekly, and monthly averages and in Gallup.com stories. Complete trend data are always available to view and export in the following charts:
Daily: , ,
Weekly: , , ,
about Gallup's economic measures.
our economic release schedule.
Survey Methods
优蜜传媒classifies American workers as underemployed if they are either unemployed or working part time but wanting full-time work. The findings reflect more than 18,000 phone interviews with U.S. adults aged 18 and older in the workforce, collected over a 30-day period. Gallup's results are not seasonally adjusted and tend to be a precursor of government reports by approximately two weeks.
Results are based on telephone interviews conducted as part of 优蜜传媒Daily tracking from Jan. 16-Feb. 15, 2011, with a random sample of 18,082 adults, aged 18 and older, living in all 50 U.S. states and the District of Columbia, selected using random-digit-dial sampling.
For results based on the total sample of national adults, one can say with 95% confidence that the maximum margin of sampling error is 卤1 percentage point.
Interviews are conducted with respondents on landline telephones and cellular phones, with interviews conducted in Spanish for respondents who are primarily Spanish-speaking. Each daily sample includes a minimum quota of 200 cell phone respondents and 800 landline respondents, with additional minimum quotas among landline respondents for gender within region. Landline respondents are chosen at random within each household on the basis of which member had the most recent birthday.
Samples are weighted by gender, age, race, Hispanic ethnicity, education, region, adults in the household, cell phone-only status, cell phone-mostly status, and phone lines. Demographic weighting targets are based on the March 2010 Current Population Survey figures for the aged 18 and older non-institutionalized population living in U.S. telephone households. All reported margins of sampling error include the computed design effects for weighting and sample design.
In addition to sampling error, question wording and practical difficulties in conducting surveys can introduce error or bias into the findings of public opinion polls.
For more details on Gallup's polling methodology, visit .
